
Bitumen Specifications

Bitumen Characteristics
In order to specify the components of Bitumen different methods are used and in most of these methods Bitumen solved in sulfur-carbon is divided into three major parts:
– Carbon: the part which is insoluble in tetrachloride carbon
– Asphaltene: insoluble part in solvents such as light aliphatic hydrocarbons such as ether
– Malton: solved part in light aliphatic hydrocarbons such as heptane. Maltons are divided into two minor groups, resins, and oils, and while resin materials are brown and semi-hard, they provide Bitumen flexibility and adhesiveness. Heavy oils make Bitumen soft, the more its amount the softer Bitumen will be.
The kind and the percentage of the mentioned materials depend completely on the oil or mineral basis of the Bitumen and the percentage of these materials can be changed with the help of their oxidation process.
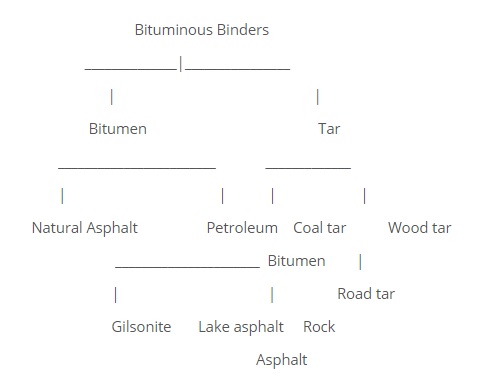
General classification of Bitumen is presented in the following table:
The amount of Bitumen in rock asphalt (stone Bitumen) is changed from 7 up to 80 percent. In Iran, rock asphalt has 70 to 80 percent Bitumen.
Total characteristics of produced Bitumen in this company are as follows:

Weight decrease percentage after 5 hours in 163-degree centigrade 0.1
In the world, more than seven kinds of Bitumen are produced which depends on climate and region conditions, but in Iran, Bitumen production is limited to two kinds due to high expenses. At present 85/100 Bitumen with high penetration and 60/70 with less penetration is produced. According to this classification in cold places 85/100 and in warm places 60/70 Bitumen is used.
The Bitumen flexibility makes asphalts lose their resistance in cold and hot climates. In desert regions, cold nights make asphalt contract and the warmth of its days separates its components and the asphalt breaks.
In many countries in order to increase the Bitumen flexibility, the polymer is added to it. In this way, they increase the flexibility of the Bitumen. The production of multi grit Bitumen in developed countries isn’t an extraordinary or hard affair. They know that for five-year Bitumen shouldn’t be repaired or dug, and they increase the life of asphalt to 20 years in this way, and never ignore its repair and maintenance.
Besides Bitumen type, roadbed and preparation of asphalt bed is also important. In making asphalt, 4 to 5 percent Bitumen and 96 percent other materials are used; many of the faults lie on drainage, improper roadbed, neglecting region traffic volume and uncoordinated fulfillment of the project. The method of fulfillment in asphalt section is not according to established principles, and in order to gain more benefit, most of the norms are disregarded.
Petroleum Bitumen Specifications
1) Penetration degree: Penetration test is used to determine bitumen hardness. In this test, a standard needle under the influence of a 100-gram load penetrates into bitumen at 25 ° C for 5 seconds. The penetration value in terms of the tenth of millimeters is called penetration degree. The lower the degree of penetration is, the harder the bitumen will be.
2) Viscosity: The higher the bitumen viscosity is, the higher solid properties it shows. Clearly, at lower temperatures, the viscosity is smaller. This property of bitumen characteristic is measured using the Saybolt Furol machine or by the kinematic method.
3) Flash point: The Flash point is the temperature that, if the bitumen reaches that temperature, the resulting gases will ignite when the flame approaches, and a flame occurs at its surface. The maximum temperature at which the bitumen can be heated in the workshop is limited to the flash point.
4) Weight loss on heating: The weight loss of bitumen at high temperature is due to the evaporation of a part of its oil and its petroleum compounds. This characteristic is also of significant properties of bitumen. The weight loss of bitumen is measured at the temperature of 163° C and within 5 hours (approximate conditions for cooking asphalt).
5) Ductility: If we pull a sample of bitumen with a cross-section of 1 cm 2 at a speed of 5 cm / min, we increase the length of the sample before tearing the ductility property of bitumen.
6) Solubility in CS2: We know the solvent of bitumen is carbon tetra-chloride and carbon-sulfur. So, if we dissolve a sample of bitumen in each of these materials, its impurities remain, and we can determine the purity of bitumen. The degree of purity is: (sample bitumen weight) ÷ [(impurity weight) – (bitumen weight)]
7) Softening point: The softening point is the temperature when the bitumen reaches that temperature, the bitumen becomes fluid. The higher the bitumen softening point, the lower the sensitivity to temperature variations. The softening point of ordinary bitumen is about 60 to 70.
